Ayurvedic Management of Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP) in Kids
Abstract
We all were kids once. And what did we get most excited about as kids? Nothing as refreshing and fun like playing outdoors with other children our age, right ? Lots of shared laughter, inside jokes, cycling around the town with friends and of course, some scratches on legs and arms from when we fell down. But we did not let those scratches come in the way of fun and often forgot about those in a minute or two when they stopped bleeding. Ever wondered how the blood came to stop flowing in such a short time? The mechanism that prevents the blood from oozing out continuously is called Clotting. Clotting is like your body’s emergency “leak-fix” crew- the moment a blood vessel gets damaged, tiny platelet “construction workers” rush to the scene, throw up a fibrin “mesh fence,” and patch the hole so you don’t spring a permanent leak.
When this clotting mechanism does not work, the bleeding does not stop and this may land the patient in a critical state. One such auto-immune condition is Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP). It is a condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own platelets, the tiny cells responsible for blood clotting. This leads to a lower platelet count, making bruising, bleeding gums, or tiny red skin spots more common. This condition, if diagnosed timely, is easily manageable and prevents unnecessary blood loss. In rare cases, it may cause death, mainly in cases of intracranial hemorrhage.
Introduction
Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP) is an auto-immune disease that primarily affects children between 2 and 6 years of age. It is a blood disorder characterised by low platelet count in blood, easy bruising and frequent bleeding that does not stop. In ITP, autoantibodies bind to platelets, leading to their premature destruction predominantly in the spleen. Parents usually discover that prolonged bleeding time and clotting time is seen. Bleeding time is the time taken for bleeding to stop and in people without ITP, it normally ranges between 2-7 minutes. While, the clotting time is the time taken for blood to transform from liquid to a clot after being removed from the body. Clotting time is normally between 8-15 minutes in healthy individuals. Low platelet count can cause excessive bleeding, both internally and externally.
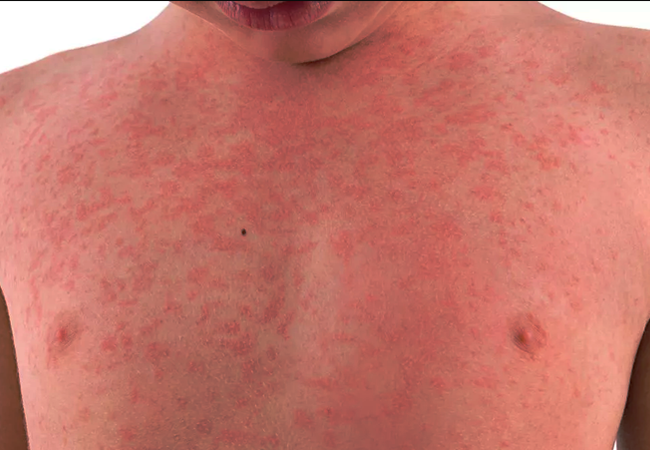
Types
Generally, it is classified into two types
- Acute and Chronic ITP.
1. Acute Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura
Acute Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura- This type is found in young children (2-6 years) and starts very abruptly and the symptoms are experienced for less than 6 months. Sometimes, the symptoms go away on their own without needing any treatment.
2. Chronic Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura
Chronic Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura- No specific age range is seen in these cases. This can appear at any age and the symptoms usually stay for about a year. Females are more prone to this.
We can further classify on the basis of cause- Primary and Secondary ITP.
- Primary ITP- Auto-immune response of the body due to unknown causes.
- Secondary ITP- This type is associated with certain medical conditions or viral infections like HIV or Hepatitis.
Causes of ITP
In primary ITP no exact cause is known.
Secondary ITP can occur due to variety of reasons like-
- Viral and Bacterial infections- HIV, Hepatitis C virus, Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), Cytomegalovirus (CMV), Varicella-zoster virus, Measles, Mumps, Rubella, Helicobacter pylori, sepsis.
- Autoimmune disorders- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome, Rheumatoid arthritis, Sjögren’s syndrome.
- Drug induced ITP- Heparin, Penicillin, NSAID’s.
Symptoms of ITP
Some children do not suffer from any symptoms. And in other children, the symptoms that can be seen are as follows –
- Petechiae- Tiny red dots seen under the skin.
- Purpura- Purple discoloration of the skin .
- Epistaxis- Bleeding from the nose.
- Bruising- Very easily bruised. Bruising can appear on knees and elbows just from movement.
- Bleeding gums.
- Bleeding around the mouth is also seen.
- Bleeding in stools or urine can be seen.
- In females, heavy menstrual bleeding is seen.
- Hematemesis- Vomiting with blood mixed in it.
- Internal bleeding- It does not reveal itself on the surface and is usually diagnosed with low platelet count found in blood analysis test reports.
- Fatigue and weakness.
Diagnosis
- Physical Examination- Red spots, bruising, bleeding is seen.
- Coagulation profile.
- Complete Blood Count- Platelet count less than 10000 per microliter in children.
- Peripheral smear- To analyse morphology and number of blood cells.
- Bone Marrow Aspiration- To know the number of platelets produced and to check for any abnormality. This is rarely used.
Treatment
While some children may not need any treatment, a check on platelet count should be kept.
In rest, medicines to boost platelet production and count are given, and also to slow down destruction of platelets.
- Rituximab- protects platelets from destruction.
- Dexamethasone- Given in high dose, to promote platelet production.
- Corticosteroids- Decreases platelet destruction and increases platelets twice in number in a week.
- Intravenous immunoglobulin- Works faster than steroids in preventing destruction.
- Splenectomy- Removal of spleen to avoid destruction of platelets.
Ayurvedic Overview
In Ayurveda, ITP is correlated with Raktapitta (bleeding disorders), more specifically, Tiryaga Raktapitta. It is a Pittaja vyadhi (disease) and refers to a group of disorders resulting from the vitiation (Dushti) of Pitta dosha. Pitta governs digestion, metabolism, vision, complexion, intellect, and body temperature. This aggravated Pitta induces pathological changes primarily in Rakta dhatu (blood tissue) and subsequently in other tissues, manifesting as various heat-related and inflammatory disorders.
Causes of Tiryaga Raktapitta includes
1. Aahara Hetu (Dietary Causes):
- Excessive intake of Amla rasa (sour-tasting foods).
- Excessive intake of Katu rasa (pungent-tasting foods).
- Excessive intake of Lavana rasa (salty foods).
- Foods having Ushna guna(hot potency).
- Viddahi ahara (foods causing burning sensation and acidity).
- Fermented and putrefied foods.
- Excessive consumption of Madya (alcohol).
- Atibhojana (Overeating ).
- Intake of incompatible food combinations (Viruddha ahara).
2. Vihara Hetu (Lifestyle Causes)
- Exposure to Atiushna (excessive heat or strong sunlight).
- Vega Dharana (Suppression of natural urges).
- Divaswapna (Daytime sleeping).
- Ativyayama (Excessive exercising).
3. Maansika Hetu (Psychological Causes)
- Krodha (Excessive anger).
- Mental stress
- Kala Hetu (Seasonal & Environmental Causes)
Seasonal aggravation of Pitta during Autumn (Sharada Ritu).
1. Living in hot climates.
When these causative factors are indulged in repeatedly, Pitta dosha becomes aggravated and enters Rakta dhatu (blood tissue), increasing its heat and fluidity. This vitiated blood moves in abnormal directions and seeps through Srotas (channels), leading to bleeding in both Urdhavaga (upwards direction) and Adhoga marga (Downwards direction).
If we discuss about its lakshana ( symptoms), we can see the following:
Bleeding from Urdhava Marga (Upward bleeding)- Nasa srava (nosebleeds), Mukha srava (bleeding from mouth), Netra srava blood discharge from eyes), Karna srava (bleeding from nose), Raktavamana (hematemesis). Bleeding from Adho Marga (Downward bleeding)- Gudasrava (rectal bleeding), Mutra srava (hematuria), Artava srava (excessive menstrual bleeding). These symptoms can be relieved using Ayurvedic protocol. Treatment principles in Ayurveda involves- Langhana (Fasting), Tarpana (Nourishment therapy) and some classical formulations like Kharjooradi Tarpan, Laja Tarpan, Padmautpalaadi Peya, Priyangavaadi Lepa, Shatavari Ghrita and Panchpanchmoola Ghrita.
In case of epistaxis (Bleeding from nose), a few drops of Dooba plant (Bermuda grass) should be given in the form of Nasya (Nasal administration therapy) to stop bleeding immediately. Samshodhana therapy in the form of Vamana (therapeutic emesis) and Virechana (therapeutic purgation) is very useful in patients with good shareera bala (physical strength) and good mansika bala (mental strength).
Dietary Habits and Lifestyle Modifications
- Follow Diet- Fruits such as apples, papaya, pomegranate, bael, kiwi, and watermelon are recommended. Suitable vegetables include potatoes, cauliflower, cabbage, bottle gourd, pumpkin, round gourd, broccoli, beetroot, carrot, and all fresh leafy greens. Whole grains like millets and wheat flour can be consumed. Soaked almonds, walnuts, and raisins are also beneficial.
- Avoid Diet- Avoid milk and dairy products, citrus fruits (e.g., lemon, orange), and vegetables such as onion, garlic, ginger, tomato, eggplant, and capsicum. White refined flour should be strictly excluded. Dry fruits and seeds like pistachios, cashews, flax seeds, sunflower seeds, and chia seeds should also be avoided.
- Water intake- Adequate hydration should be maintained. An average of 2.5-3 litres of water/day should be taken.
- Yogansana and Pranayama techniques- Vajrasana, Tadasana, Balasana, Shavasana are beneficial in ITP patients. These asanas are not strenuous and improve blood circulation. Anuloma-Viloma (Alternate Nostril Breathing) and Bhramari (Bee Breath) should be practised by ITP patients.
- Physical exercise- No demanding physical activities should be done by the patients.
Herbal Remedies for ITP in kids by Planet Ayurveda
Planet Ayurveda is a globally trusted herbal manufacturing company committed to delivering pure, natural, and authentic Ayurvedic formulations. Established with the vision of reviving the ancient healing wisdom of Ayurveda guided by a team of experienced Ayurvedic doctors, it provides effective treatment for various health conditions. ITP Care Pack for kids comprises eight medicines, working together to provide relief from ITP symptoms and naturally boosting platelet production in the body. This pack includes-
- Giloy Capsules
- Ashwagandha Capsules
- Gandhak Rasayan
- Immune Booster
- Kumar Kalyan Ras
- Infee Syrup
- Arvindasav Syrup
- Praval Panchamrit
Product Description
Giloy Capsules are prepared from Giloy (Tinospora cordifolia) which is one of Ayurveda’s most valued herbs, traditionally known as Amrita due to its powerful rejuvenating and immunity-boosting properties. It helps balance all three doshas (Vata, Pitta, Kapha). It is valued for supporting platelet count recovery, enhancing the body’s defense making it useful in various immune-mediated disorders.
Dosage– 1 capsule twice daily
Ashwagandha Capsules– These capsules are made from Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera), which is a renowned Rasayana in Ayurveda, prized for its rejuvenating and adaptogenic properties. It balances Vata and Kapha dosha. It reduces inflammation, and enhances hematopoiesis. In Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP), it helps regulate immune responses, minimizes stress-induced platelet decline, and improves energy levels.
Dosage – 1 capsule twice daily.
Gandhak Rasayan– These tablets are prepared from purified Sulphur (Shuddha Gandhak). It helps by purifying the blood (Raktashodhaka), reducing inflammation and balancing Pitta and Kapha doshas. It aids in maintaining healthy skin, reducing petechiae, and promoting overall vitality in platelet-deficient conditions.
Dosage – 1 tablet once daily.
Immune Booster– These capsules have key ingredients like grape seed (Vitis vinifera), Go – Piyush (Bovine colostrums), Bhumi amla (Phyllanthus niruri) and Amalaki (Emblica officinalis). It protects platelets from oxidative damage, reduces bruises and petechiae, and also promotes blood tissue health.
Dosage – 1 capsule twice daily.
Kumar Kalyan Ras– This tablet is a classical formulation with key ingredients like Kumari Swaras (Aloevera juice), Rasa Sindoor (Mixture of purified Mercury and Sulphur), Swarna Bhasma (Gold calyx) and Mukta Pishti (Pearl calyx). All these components work on the overall immunity in children and help with symptoms like fatigue, weakness, loss of appetite, fever by balancing both Vata and Kapha doshas.
Dosage- 1 tablet once daily.
Infee Syrup– This herbal syrup contains Yashtimadhu (Glycyrrhiza glabra), and Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia). Both these boost immunity, reduce inflammation and improve appetite. Guduchi is especially beneficial in combating fevers in kids with ITP.
Dosage– 2 teaspoons twice daily.
Arvindasav Syrup– This syrup contains key ingredients like Yashtimadhu (Glycyrrhiza glabra) and Nagarmotha (Cyperus rotundus). Both these herbs are of cool potency and are extremely helpful in pacifying fever in ITP patients.
Dosage – 2 teaspoons twice daily.
Praval Panchamrit Ras – This tablet is a classical Ayurvedic herbo-mineral formulation primarily used for Rakta Pitta disorders. Key ingredients are Praval Bhasma (Coral calyx), Shuddha Shilajit and Gandhak (Purified Sulphur). It purifies blood, rejuvenates the body and pacifies Pitta dosha, relieving symptoms of ITP.
Dosage– 1 tablet twice daily.
Conclusion
Managing Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP) in children through Ayurveda focuses on keeping the Pitta dosha in balance while nourishing the blood (Rakta Dhatu) and boosting the immune system. Gentle herbal remedies like Giloy, Ashwagandha, and Guduchi play a big role- they help protect platelets, reduce inflammation, and support overall vitality. Ayurvedic Rasayana therapies further strengthen the body and promote natural healing. Alongside herbs, a dosha-friendly diet is important- warm, light, and easily digestible foods help the body function better. Lifestyle habits like regular sleep, moderate activity, and stress-free routines also support recovery. The holistic approach of Ayurveda doesn’t just aim at improving platelet count; it helps prevent excessive bleeding, restore energy, and support healthy growth and development. Overall, it provides a safe, natural, and nurturing way to help children with ITP feel stronger and healthier. It is important to consult an Ayurvedic physician if you are experiencing these symptoms or someone you know have been experiencing it.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
1. How serious is ITP in children?
While ITP may sound worrying to parents but in most children the condition will settle down quite quickly– often without needing any treatment. The platelet count is often up to safe levels within a week or two, but it may take longer to fully return to normal.
2. Is ITP a bone marrow disorder?
No, there is no specific research confirming this. Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) is an autoimmune disorder characterised by platelet destruction and suppressed platelet production. In the bone marrow examinations of patients with ITP, some investigators found megakaryocyte numbers to be increased while others have found them to be normal.
3. Is ITP like leukemia?
While the symptoms are relatively similar. The primary treatment given and the response to it helps in differentiating ITP from leukemia.
4. Can ITP happen suddenly?
Acute ITP usually has a very sudden onset and the symptoms usually disappear in less than six months (often within a few weeks). It doesn’t reoccur in almost 90% of cases.
5. What is the emergency treatment for ITP?
Treatment strategies are generally based on the condition of the patient. Cases with plummeting platelet count require immediate platelet transfusions.
6. What happens if ITP is not treated?
If ignored, platelet count keeps going to the lower side. The lower your count, the more likely you are to have spontaneous and unexpected bleeding, both internally and externally. Without treatment to correct platelet counts, bleeding can become severe and life threatening.
7. What disease is similar to ITP?
Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) are both blood disorders that affect platelets and may exhibit similar symptoms, such as unexplained bruising, bleeding, and fatigue.







