Fatty Liver And Its Ayurvedic Management
Abstract
Fatty liver disease is a common hepatic condition characterized by the abnormal accumulation of fat within liver cells. It is closely associated with a sedentary lifestyle, obesity, diabetes, excessive alcohol intake, and metabolic disorders. In Ayurveda, this condition can be correlated with Yakrit Roga involving Kapha and Pitta dosha vitiation, along with Medo Dhatu dushti. If left untreated, it may progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and even hepatocellular carcinoma. Early diagnosis, lifestyle modification, dietary regulation, and herbal formulations play a crucial role in prevention and management.
Introduction
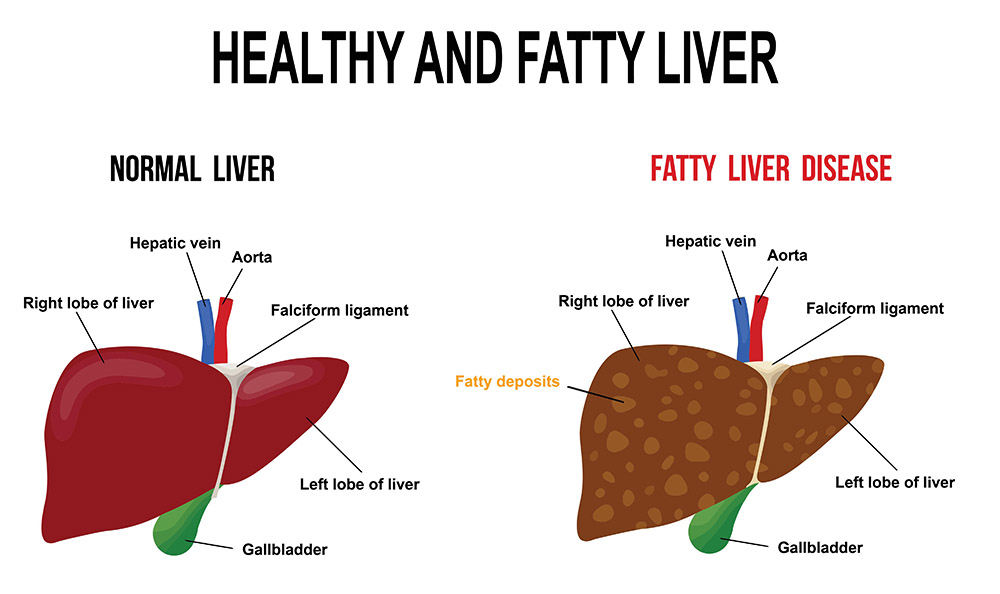
The liver is the largest internal organ of the human body. It plays a vital role in digestion by processing nutrients from food, storing energy for later use, and detoxifying harmful substances such as poisons, alcohol, and drugs to keep the body healthy. Fatty liver is a condition that develops when there is an excessive accumulation of fat in the liver cells. Generally, it is normal for the liver to contain some fat, but if the fat accumulation is more than 10 percent of the liver’s weight, then it is suggestive of fatty liver. This excess fat accumulation may lead to inflammation of the liver.
Two Types Of Fatty Liver
Fatty liver disease is mainly categorised into types:
- Alcoholic fatty liver disease
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Causes
The causes of fatty liver disease can be categorized as:
1. Causes of alcoholic fatty liver disease: This condition only occurs in individuals with excessive and prolonged intake of alcohol.
2. Causes of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: The exact cause of NAFLD is still unknown. This condition may develop in individuals having type 2 diabetes, obesity, high blood pressure, high-fat diet intake, hormonal imbalance such as PCOS, thyroid, or some drugs like cholesterol, etc.
Symptoms
Fatty liver disease is usually a silent disease with few or no specific symptoms. In some individuals, symptoms such as discomfort or pain in the upper right part of the abdomen, weight loss, tiredness, itching, or generalised weakness may occur.
Diagnosis
- A detailed medical history is taken, which includes questions about existing health conditions, alcohol consumption, and current medications.
- Physical examination to look for signs of inflammation, such as an enlarged liver, and features of cirrhosis, including jaundice.
- Blood tests, such as liver function tests, may help to rule out any inflammation.
- Imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scan (computed tomography), or MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) are often used to evaluate the liver for inflammation and scarring.
- In addition, a liver biopsy (removal of a small tissue sample) may be performed to assess the extent of liver damage.
Modern Treatment
Management of fatty liver disease mainly emphasizes lifestyle modification, weight management, and consuming a healthy diet. There are no specific medications recommended for fatty liver; treatment targets mainly the associated symptoms or diseases like diabetes, obesity, etc.
Ayurvedic Overview
In Ayurvedic texts, the liver is considered an important organ, referred to as the word “Yakrit” (यकृत्). When Pitta Prakopaka Nidana, such as Ati-ushna (hot), Amla (sour), Katu (pungent), excessive intake of alcohol, etc, are consumed, the Pitta Dosha gets imbalanced. This causes disturbance in the functions of the yakrit (liver), which leads to metabolic derangements and progression of disease. In Ayurveda, a condition called Yakrit Dalludara refers to Yakrit Vriddhi, which means enlargement of the size of the liver. Due to aggravation of kapha dosha, there is heaviness in the abdomen, poor digestion, and a gradual increase in the size of the liver; this condition is termed Kaphaja Yakrit Dalludara. When meda (Adipose tissue) in the yakrit (Liver) increases, there is excess accumulation of fat in the liver, which leads to a condition called Medaja Yakrit Dalludara. This condition can be correlated with fatty liver disease.
The condition can be managed by dietary restrictions, Nidana parivarjana (avoidance of causative factors), including deepan pachana (digestive) drugs, medohar drugs to reduce fat accumulation, and detoxifying therapies like virechan (Purgation therapy) and basti (Enema).
Ayurvedic Herbs Used In Fatty Liver Disease
1. Triphala (Haritaki, Bibhitaki, Amalaki)
Triphala has properties like Deepana (enhances digestive fire), paachana (digestion), lekhana (therapeutic scraping), and anulomana (mild purgative). These guna (properties) of Triphala will eliminate Aama (toxins) and reduce accumulation of fat in the liver.
2. Kalmegh (Andrographis paniculata)
Due to its katu vipaka and ushna veerya, the drug acts as pittasaraka (elimination of pitta dosha). It is also considered as Yakrituttejaka, stimulates liver functions such as lipid metabolism and thus reduces the excess accumulation of cholesterol and triglycerides.
3. Bhumi Amla (Phyllanthus niruri)
It contains flavonoids and lignans, which protect the liver cells from damage. Tikta rasa (bitter taste), Sheeta veerya (potency) and madhura vipaka pacify pitta dosha.
4. Kutki (Picrorhiza kurroa)
Lekhana (scraping) action of kutaki eliminates the excess fat and kapha dosha accumulation in the liver. It also acts as a pittavirechaka (bile eliminating) and thus stimulates the secretions of bile.
5. Bhringraj (Eclipta alba)
This drug acts as Yakrituttejaka which stimulates the liver functions, does rechana of the pitta dosha and pachana of aama (toxins). Its chemical constituents, like ecliptasaponins, wedelolactone, and coumestans, protect the liver cells from the accumulation of fat and toxins.
6. Sharpunkha (Tephrosia purpurea)
This drug is called Pleehashatru or Pleehavridhinashaka and is used in enlargement of liver and spleen. It reduces the fat deposition in the liver by its ushna veerya (potency) and katu vipaka. Its constituents, like rotenoids and flavonoids, act as antioxidants and an anti-inflammatory which protects the liver cells from damage.
7. Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia)
Helps in liver detoxification and pacifies pitta and kapha dosha. Giloy (Tinospora cordifolia) helps in fatty liver by reducing excess Pitta and balancing metabolism, aiding in detoxification. In Ayurveda, it acts as a Rasayana (rejuvenative) herb that improves liver function and promotes healthy digestion.
8. Turmeric (Curcuma longa)
Its bitter (Tikta), pungent (Katu) taste, and hot (Ushna) properties balance pitta and kapha doshas. It is useful in healing liver cells which get injured due to fat deposition. It also acts as a Yakrit Rasayana, thus rejuvenating the liver.
Lifestyle And Dietary Management
Foods To Add
- Cereals and pulses: Old rice, wheat, barley, oat, green gram, red gram
- Spices: Fenugreek, clove, cardamom, curry leaf, black pepper
- Fruits: Apple, draksha, kiwi, fig, pomegranate, papaya
- Vegetables: Moringa, radish, tomato, carrot, beet root, patola, jeevanti, punarnava
- Others: Ghee, milk, butter milk, etc
Foods To Avoid
- Cereals and pulses: Rice flour, new rice, chick pea, kidney pea
- Spices: Cinnamon, excess salt
- Fruits: Banana, mango etc
- Vegetables: Pumpkin, sweet potato, potato, cabbage
- Others: Curd, cheese, soda, cold drinks
Pranayama (breathing exercise) such as kapalabhati, yoga like gomukhasana (Cow Face Pose), Ardha matsyendrasana (Half Lord of the Fishes Pose), Dhanurasana (Bow pose) and meditation (dhyana) will help in the management of this condition.
Herbal Remedies For Fatty Liver Disease By Planet Ayurveda
Planet Ayurveda offers a carefully formulated combination of effective herbal remedies for the Ayurvedic management of fatty liver. These formulations are prepared using high-quality herbs while strictly adhering to the classical principles of Ayurveda. Being pure, natural, safe, and side-effect-free, they provide a holistic approach to supporting liver health and restoring balance naturally.
Product Description
1. Yakrit Plihantak Churna
This is a classical Ayurvedic herbal powder prepared from a combination of potent liver-supporting herbs. It contains herbs such as Bhumiamla (Phyllanthus niruri), Katuki (Picrorhiza kurroa), Punarnava (Boerhavia diffusa), Kalmegh (Andrographis paniculata), etc. The herbs in this formulation do rechana (eliminate) of pitta dosha, reduce excess fat accumulation by its lekhana property and also helps in rejuvenation of liver.
Dosage: 1 teaspoonful twice daily, taken before meals with warm water, or can be consumed as a decoction.
2. Livo Plan Syrup
It is a herbal formulation prepared from the standardized extracts of liver-protective herbs. It contains Bhringraj (Eclipta alba), Sharpunkha (Tephrosia purpurea), Kalmegh (Andrographis paniculata), Shyonak (Oroxylum indicum), Rohitaka (Tecomella undulata), Bhumiamla (Phyllanthus niruri), Patol (Trichosanthes dioica), etc. This formulation acts as a tonic which stimulates liver functions, removes ama (toxins), and prevents the liver from damage.
Dosage: 2 tsp twice a day after meals.
3. Liver Detox Formula
This is a polyherbal capsule formulation enriched with powerful hepatoprotective herbs such as Kutki (Picrorhiza kurroa), Punarnava (Boerhavia diffusa), Makoy (Solanum indicum), Himsra (Capparis spinosa), and Kaasni (Cichorium intybus). The drugs present in this formulation act as pittavirechaka, eliminate pitta and kapha dosha, cleanse and provide strength to the liver. These drugs also maintain the hormone level in the liver by removing toxins from the liver.
Dosage: 1 capsule twice daily to be taken after meals with warm water.
Conclusion
Fatty Liver Disease is mainly due to the vitiation of kapha and meda dosha, usually associated with pitta dushti. Fatty liver treatment as per Ayurveda mostly includes Nidana Parivarjana, which means avoiding the factors that cause the disease, consuming pathya ahara in the diet for fatty liver disease, stimulation of agni with carminative drugs, using medohara drugs for the correction of meda dhatu metabolism, and cleansing procedures like basti and virechana to balance the dosha. Rasayana therapy is also recommended for restoring the normal function of the liver.






